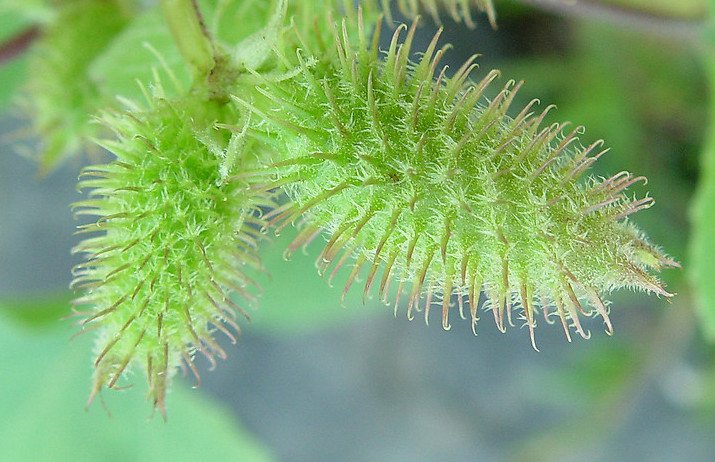
Cocklebur (Xanthium strumarium) might seem like just another weed dotting the landscape, but it’s the source of troublesome allergic reactions for some individuals. Recognizable by its spiny burrs that cling to clothing and animal fur, cocklebur thrives in various environments, making it a pervasive presence. We will discuss everything about cocklebur allergy, shedding light on how this common plant can impact health and of course, offering tips and advice on how to minimize its effect in order to live a truly Allergy-free Lifestyle!
What is Cocklebur?
Cocklebur is a hardy annual plant known for its resilience and ability to spread rapidly. While it plays a role in the ecosystem, cocklebur’s growth can become problematic due to its allergenic properties and the physical hazards posed by its burs.
Cocklebur is a fascinating plant with a dual identity; on one hand, it’s considered a tenacious weed, while on the other, it plays a role in its ecosystem. Originating from a genus of flowering plants in the Asteraceae family, cocklebur is easily recognized for its distinctive features and ability to thrive in a variety of environments.
Habitat and Appearance
Cocklebur typically grows in disturbed soils, which are common in agricultural lands, riverbanks, and roadsides. Its adaptability allows it to populate areas across temperate and tropical zones worldwide, making it a ubiquitous presence in both rural and urban settings. The plant can reach heights of up to 4 feet, featuring broad, heart-shaped leaves and a robust stem.
One of cocklebur’s most notable characteristics is its fruit – a hard, spiny bur that encases seeds. These burs are designed to latch onto the fur of animals or the clothing of humans, facilitating the spread of seeds over great distances. While this mechanism is effective for propagation, it can also contribute to the plant’s invasive nature, allowing it to colonize new areas rapidly.
Cocklebur’s Ecological And Invasive Role
Despite its reputation as a weed, cocklebur plays a significant ecological role. Its seeds serve as a food source for various birds and small mammals, such as Goldfinches and Sparrows, while its dense growth can provide shelter for wildlife. However, the plant’s rapid proliferation and robust nature often lead to challenges in managing agricultural lands and natural habitats. Cocklebur’s ability to compete with crops and native plants for resources, coupled with the difficulty in removing its resilient burs from soil and fur, underscores the nuisance factor associated with this plant.
Moreover, cocklebur is known to produce toxic compounds, particularly in its seedlings, which can pose risks to livestock if ingested. This toxic aspect adds another layer of complexity to the plant’s management, especially in areas where animals graze.
The toxic substance found in cocklebur (Xanthium sp.) is primarily carboxyatractyloside. This compound is a potent toxin that affects the liver and can lead to liver failure in various animals, including livestock such as cattle, horses, and pigs, if they consume significant amounts of the plant, especially the most toxic seedlings. Carboxyatractyloside interferes with cellular energy production by inhibiting the process of ADP-ATP exchange in mitochondria, which is crucial for cell energy production.
Minimizing cocklebur’s spread
Understanding cocklebur’s characteristics, habitat, appearance, ecological role, and potential as a nuisance is crucial for effectively managing and preventing unwanted proliferation. By recognizing areas prone to cocklebur growth, individuals who are allergic or suspect an allergic reaction from cocklebur can take proactive steps to control its spread, such as regular monitoring and removal before the plants mature and release their burs while taking the appropriate protective measures.
Educational efforts can also raise awareness about the risks associated with cocklebur, including its allergenic pollen and potential toxicity.
It’s still important to note that while cocklebur may be seen primarily as a weed, its presence in various ecosystems worldwide speaks to its adaptability and resilience. Balancing its management while not forgetting its ecological role requires a fine understanding of what cocklebur truly is—a plant with beneficial and allergic, toxic attributes.
Cocklebur Allergy

Allergies are the immune system’s response to foreign substances, known as allergens, that are perceived as threats. Plant-based allergens like cocklebur can trigger a reaction triggered by pollen or contact with the plant’s burs. Understanding the body’s allergic response is crucial for identifying and managing allergies effectively.
Cocklebur Allergy Symptoms and Triggers
Cocklebur allergy occurs when individuals are sensitive to the pollen or, less commonly when they are in contact with the plant and react to its allergenic components. Understanding the symptoms and triggers of cocklebur allergy is crucial for those affected, as it allows for better management and avoidance of exposure.
Symptoms of Cocklebur Allergy
Allergic reactions to cocklebur generally manifest in ways similar to other pollen allergies, with symptoms ranging from mild to potentially severe. Common symptoms include:
- Nasal Symptoms: Sneezing, runny or stuffy nose, and postnasal drip.
- Ocular Symptoms: Itchy, red, swollen, or watery eyes and sometimes, eye floaters.
- Respiratory Symptoms: Wheezing, coughing, or difficulty breathing, particularly in individuals with pre-existing respiratory conditions like asthma.
- Skin Reactions: Contact with cocklebur plants can sometimes cause skin irritation or hives, particularly in individuals with sensitive skin or those with a direct allergic reaction to the plant material.
These symptoms can significantly impact the quality of life, especially when cocklebur is actively pollinating.
Triggers of Cocklebur Allergy
The primary trigger for cocklebur allergy is the inhalation of pollen released by the plants during their flowering season, which typically spans late summer to early fall. Cocklebur pollen can travel through the air over considerable distances, making it challenging to avoid for individuals living in areas where the plant is prevalent.
- Environmental Factors: High pollen counts, especially on windy days or during specific times of the year when cocklebur is in bloom, can exacerbate symptoms. Humidity and rain can also affect pollen levels, with damp conditions temporarily reducing airborne pollen but potentially leading to bursts of pollen release on subsequent warm, dry days.
- Direct Contact: In addition to airborne pollen, direct contact with cocklebur plants, especially the burs, can trigger allergic skin reactions in some individuals. While less common than respiratory symptoms, skin irritation can occur from handling the plant or coming into contact with its burs.
Managing Exposure
For those with cocklebur allergy, managing exposure is key to reducing symptoms:
- Pollen Avoidance: Keeping windows closed during high pollen times, using air purifiers, and staying indoors on windy days can help minimize exposure.
- Protective Clothing: Wearing long sleeves and gloves when gardening or in areas where cocklebur might be present can prevent skin contact.
- Awareness of Pollen Seasons: Staying informed about local pollen forecasts can help individuals anticipate and prepare for periods of high cocklebur pollen levels.
Understanding the symptoms and triggers associated with cocklebur allergy is the first step toward effective management. By recognizing the signs of an allergic reaction and taking proactive measures to minimize exposure, individuals with cocklebur allergy can better navigate their environments and maintain their health and well-being during the allergy season.
Diagnosis of Cocklebur Allergy
Diagnosing a cocklebur allergy involves a series of steps to confirm sensitivity to this particular allergen. Since symptoms of a cocklebur allergy can mirror those of other common allergies, pinpointing the exact cause requires careful investigation by healthcare professionals, typically an allergist. Here’s an in-depth look at the diagnostic process for cocklebur allergy:
Initial Consultation
The process begins with a thorough patient history and physical examination. Patients are often asked about their symptoms, when they occur, their severity, and any observed patterns or triggers. This conversation may delve into the patient’s lifestyle, including time spent outdoors and any prior history of allergies. The goal is to gather clues that suggest or distinguish a cocklebur allergy from other possible allergic reactions.
Skin Prick Test (SPT)
The Skin Prick Test is one of the most common methods for diagnosing specific allergies. During this test, a small amount of the suspected allergen, in this case, cocklebur extract, is introduced into the skin, usually on the forearm or back. If the patient is allergic to the substance, a localized reaction typically occurs within 15 to 20 minutes, manifesting as a raised, red bump similar to a mosquito bite.
- Specificity to Cocklebur: Since cocklebur is not always included in standard allergen panels, mentioning suspected exposure to this particular plant can help ensure it is considered during testing.
Blood Tests
Blood tests may be utilized for individuals unable to undergo skin testing or when further confirmation is needed. These tests measure the presence of specific IgE antibodies to cocklebur pollen in the patient’s blood. High levels of these antibodies can indicate a sensitization to the allergen, supporting the diagnosis of a cocklebur allergy.
- Advantages: Blood tests are less affected by skin conditions and medications that might interfere with skin testing.
- Considerations: While informative, blood tests are generally more expensive than skin tests, and results take longer to receive.
Differential Diagnosis
Because cocklebur allergy symptoms are similar to those of other respiratory allergies, part of the diagnostic process may involve ruling out other potential causes. This could include testing for common allergens like grasses, trees, and weeds pollen, as well as molds and pet dander. Identifying or excluding other allergies helps clarify the diagnosis and informs a more targeted management approach.
Management of a Positive Diagnosis
Once a cocklebur allergy is confirmed, the healthcare provider will discuss management strategies tailored to the individual’s lifestyle and the severity of their reactions. These strategies typically focus on avoidance of exposure, symptomatic relief through medication, and, in some cases, immunotherapy.
The Importance of Accurate Diagnosis of Cocklebur Allergy
An accurate diagnosis is paramount for effectively managing cocklebur allergy. It not only enables targeted avoidance strategies and treatment but also helps prevent the potential escalation of symptoms. Armed with a clear understanding of their condition, individuals can take proactive steps to minimize their exposure to cocklebur pollen and other irritants, improving their overall quality of life during allergy season.
Managing and Treating Cocklebur Allergy
Successfully managing and treating cocklebur allergy requires several approaches that combine avoidance strategies, symptomatic treatment, and, in some cases, long-term desensitization. The goal is to minimize exposure to the allergen, alleviate symptoms, and improve the individual’s quality of life. Here’s a detailed exploration of the methods involved in managing and treating cocklebur allergy:
Avoidance Strategies
Avoidance is the cornerstone of managing cocklebur allergy. Since complete avoidance of outdoor air is impractical, especially during peak pollen seasons, the following strategies can help reduce exposure:
- Stay Informed: Keep track of local pollen counts, especially during late summer and early fall when cocklebur typically pollinates. Websites, apps, and local weather forecasts can provide this information.
- Limit Outdoor Activities: On days with high pollen counts or windy conditions, try to stay indoors as much as possible. If you need to go outside, consider wearing a pollen mask.
- Create a Pollen-Free Space: Use air purifiers with HEPA filters in your home and car to reduce indoor pollen levels. Keep windows and doors closed during high pollen periods.
- Personal Hygiene: After spending time outdoors, change your clothes and take a shower to remove pollen from your skin and hair. Regularly wash bedding and clothing during pollen season.
- Garden Carefully: If you garden, wear gloves and a mask to minimize contact with cocklebur plants and other potential allergens. Consider removing cocklebur plants from your vicinity, taking care to protect your skin and respiratory system during the process.
Symptomatic Treatment
For those times when avoidance is not enough, various medications can help manage the symptoms of cocklebur allergy:
- Antihistamines: Over-the-counter or prescription antihistamines can relieve sneezing, itching, runny nose, and watery eyes by blocking the action of histamine, a substance released during an allergic reaction.
- Nasal Corticosteroids: These nasal sprays help reduce inflammation in the nasal passages, addressing congestion, sneezing, and an itchy or runny nose.
- Eye Drops: Antihistamine or anti-inflammatory eye drops can alleviate itchy, watery eyes.
- Decongestants: Available in oral or nasal spray forms, decongestants can provide temporary relief from nasal stuffiness.
Always consult with a healthcare provider before starting any new medication to ensure it’s appropriate for your situation and won’t interact with other medications you’re taking.
Long-term Management
An allergist may recommend immunotherapy for individuals with severe allergies who don’t find sufficient relief from avoidance and symptomatic treatment. This long-term treatment gradually desensitizes the immune system to the allergen through regular exposure to small, controlled doses. Immunotherapy can be administered as allergy shots (subcutaneous immunotherapy) or under-the-tongue tablets (sublingual immunotherapy), depending on the allergen and available treatments.
Lifestyle Modifications and Support
Adjusting daily routines and seeking support can also play a significant role in managing cocklebur allergy:
- Educate Family and Friends: Educating those around you about your allergy can help them take steps to reduce your exposure to cocklebur.
- Allergy-proof Your Home: Regular cleaning to remove dust and pollen, using allergen-proof mattress and pillow covers, and maintaining a humidity level below 50% can create a more comfortable home environment.
- Seek Support: Joining a support group for individuals with allergies can provide valuable tips, emotional support, and a sense of community.
Successfully managing cocklebur allergy involves a combination of personal vigilance, lifestyle adjustments, and professional medical guidance. By adopting comprehensive management strategies, individuals with cocklebur allergy can significantly reduce their exposure to the allergen, alleviate symptoms, and enjoy a higher quality of life despite their allergy.
Preventative Measures and Environmental Control for Cocklebur Allergy
Effective management of cocklebur allergy extends beyond individual actions to include broader environmental control and preventative measures. These strategies aim to reduce the prevalence of cocklebur in affected areas, thereby minimizing the allergen load in the environment. Here’s a closer look at the comprehensive approach needed for controlling cocklebur proliferation and safeguarding communities from its allergenic impact.
Understanding Cocklebur Growth
Cocklebur thrives in disturbed soils and areas with poor vegetation management. It’s often found along riverbanks, roadsides, agricultural fields, and in vacant lots. The plant’s ability to quickly colonize these areas is partly due to its burs, which attach to animals and clothing, spreading seeds over wide distances. Understanding these growth habits is crucial for developing effective control strategies.
Environmental Management Strategies
- Regular Monitoring and Removal: Early detection and removal of cocklebur plants before they flower and produce burs can significantly reduce their spread. This task requires regular monitoring of known growth areas and prompt removal of any new plants. Removal should be done with care, wearing gloves and protective clothing to avoid skin contact with the plant and potential allergic reactions.
- Habitat Modification: Altering the environment to make it less hospitable for cocklebur can prevent its establishment. This can include improving soil health, planting competitive vegetation that can outcompete cocklebur, and maintaining robust ground cover in areas prone to disturbance.
- Proper Disposal of Plants: After removal, cocklebur plants should be disposed of in a manner that prevents them from spreading. This typically involves bagging them securely and disposing of them with regular garbage, not composting, as seeds might survive and spread.
Community Involvement and Education
Engaging the community is vital for effective cocklebur control. Public education campaigns can raise awareness about the plant’s impact on allergies and the importance of controlling its spread. Community cleanup days can be organized to tackle areas with significant cocklebur growth, making the effort a collective endeavor.
- Collaboration with Local Authorities: In some cases, managing cocklebur proliferation may require collaboration with local agricultural extensions, environmental agencies, or public health departments. These organizations can provide resources, support, and guidance for large-scale control efforts.
- Use of Herbicides: Where appropriate and environmentally acceptable, the use of herbicides can be considered for controlling extensive cocklebur infestations. This approach should be undertaken with caution, following local regulations and environmental guidelines, to avoid unintended harm to other plant species or ecosystems.
Preventative Landscaping in Private Properties
Homeowners can adopt landscaping practices that deter cocklebur growth, such as:
- Maintaining Healthy Lawns and Gardens: Regular mowing, weeding, and maintenance of outdoor spaces reduce the chances of cocklebur establishment.
- Choosing Competitive Plant Species: Planting dense, fast-growing species that can outcompete cocklebur for resources such as light, water, and nutrients.
- Soil Health: Improving soil health through organic amendments and proper watering practices can promote the growth of desired vegetation over weeds like cocklebur.
Conclusion: Navigating Life with Cocklebur Allergy
The journey to understanding and managing cocklebur allergy is multifaceted, intertwining individual vigilance, medical intervention, and community-driven environmental controls. As we’ve explored the nature of cocklebur and its potential to trigger allergic reactions, it’s clear that awareness and proactive management are key to minimizing its impact on those affected. The conclusion of this exploration is not just a summary of facts but a call to action and a beacon of hope for individuals navigating life with cocklebur allergy.
FAQs About Cocklebur Allergy
1. How can I identify a cocklebur plant to avoid it?
Cocklebur plants are characterized by their rough, heart-shaped leaves, sturdy stems, and distinctive, spiny burs that carry their seeds. These burs are often the most recognizable feature, as they easily cling to clothing and animal fur. Familiarizing yourself with images of cocklebur can help you identify and avoid these plants during outdoor activities.
2. What times of year is cocklebur allergy most common?
Cocklebur typically flowers and releases pollen from late summer to early fall, which is when individuals with a cocklebur allergy are most likely to experience symptoms. However, the exact timing can vary based on your geographical location and the local climate.
3. Are there any home remedies to alleviate symptoms of cocklebur allergy?
While home remedies cannot cure allergies, some may help alleviate symptoms. Nasal irrigation with saline solution can reduce nasal congestion, and cool compresses can soothe itchy eyes. However, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare provider for recommendations tailored to your specific symptoms and to ensure these remedies are safe and effective for you.
4. Can cocklebur allergy lead to more severe health issues?
In most cases, cocklebur allergy symptoms are mild to moderate and can be effectively managed with avoidance and medication. However, individuals with severe allergies or asthma may experience more significant reactions, such as difficulty breathing. It’s crucial to monitor symptoms closely and seek medical attention if they worsen or if you experience signs of anaphylaxis, a potentially life-threatening allergic reaction.
5. How can I safely remove cocklebur plants from my property?
When removing cocklebur plants, wear protective gloves and long sleeves to avoid skin contact with the plant, especially if you have sensitive skin or a known allergy. Pull the plants from the ground, ensuring you remove the root system to prevent regrowth. Dispose of the plants in a sealed bag to prevent the spread of seeds. If the infestation is large or widespread, consider consulting a professional for safe and effective removal options.
6. Should I see an allergist for cocklebur allergy?
If you suspect you have a cocklebur allergy or if over-the-counter medications do not adequately control your symptoms, consulting an allergist can provide you with a definitive diagnosis and a personalized treatment plan. An allergist can perform specific tests to confirm your allergy and recommend strategies for managing exposure and symptoms, including prescription medications or immunotherapy.
By addressing these frequently asked questions, individuals with concerns about cocklebur allergy can gain a better understanding of how to identify, avoid, and manage this condition. Empowered with knowledge and the right strategies, those affected can navigate their allergy with greater confidence and comfort.